Good knowledge sharing, in-depth analysis of the copper cable, how is good copper?
Release time:2022-02-21Click:991
Guide reading: As a result of the production of copper rod two different processes, the production of Copper Rod oxygen content and appearance is different. The copper rod produced by continuous casting and continuous casting is hot-rolled under protective conditions with oxygen content in the range of 200-500 PPM, but sometimes up to 700 PPM or more, the copper produced by this method has a bright appearance and is made from low oxygen copper rods, sometimes called polished rods.
Oxygen-free Copper Rod and Rod is the main raw material in cable industry. There are two main production methods-continuous casting and continuous rolling method and up casting method. There are many methods of producing low oxygen copper rod in continuous casting and rolling, which is characterized by that after the metal is melted in the shaft furnace, the copper liquid enters the closed mould cavity through the holding furnace, Chute and Tundish, and is cooled by high cooling intensity to form the billet, after multi-pass rolling, the low oxygen copper rod is hot-processed. The original casting structure has been broken, and the oxygen content is between 200 and 400 PPM. The oxygen-free copper rods are basically produced by up-drawing continuous casting in China. After melting in an induction furnace, the metal is continuously cast by up-drawing through a graphite mould, and then cold-rolled or cold-processed. The oxygen-free copper rods produced are cast structures, oxygen levels are generally below 20 PPM. Because of the different manufacturing processes, there are great differences in structure, oxygen content distribution, impurity form and distribution, etc. .
1. Drawing property the drawing property of copper rod is related to many factors, such as impurity content, oxygen content and distribution, process control and so on. The following are from the above aspects of the copper Rod drawing performance analysis. 1. The influence of melting mode on impurities such as s in the production of copper rod by continuous casting and rolling is that the copper rod is melted by the combustion of gas. In the process of combustion, some impurities can be reduced to some extent by oxidation and volatilization, therefore, the continuous casting and rolling method has relatively low requirements for raw materials. In the production of oxygen-free Copper Rod by continuous casting, the “Copper Green”and “Copper bean”on the surface of electrolytic copper are basically melted into the copper liquid due to melting in an induction furnace. The melting s has a great influence on the plasticity of the oxygen-free Copper Rod, which will increase the wire breaking rate.
O, S, and P are elements that produce compounds with copper. In Molten Copper, oxygen dissolves some of the copper, but when the copper condenses, oxygen hardly dissolves in the copper. The dissolved oxygen in the molten state is precipitated as copper = Cuprous oxide EUTECTIC and distributed at grain boundaries. The appearance of copper-Cuprous Oxide eutectic significantly reduced the plasticity of copper. Sulfur dissolves in molten copper, but at room temperature, its solubility drops to almost zero, and its presence at grain boundaries in the form of copper(I) sulfide significantly reduces the plasticity of copper.
3. The distribution of oxygen in oxygen-deficient Copper Rod and oxygen-free Copper Rod and its influence on oxygen content have obvious influence on the tensile property of oxygen-deficient Copper Rod. When the oxygen content increases to the optimum value, the broken wire rate of the copper rod is the lowest. This is because oxygen acts as a scavenger during the reaction with most impurities. Moderate oxygen is also conducive to the removal of hydrogen in the copper solution, the formation of water vapor overflow, reduce the formation of pores. The optimum oxygen content provides the best conditions for the wire drawing process. Distribution of oxide in low oxygen copper rod: In the initial stage of solidification in continuous casting, heat dissipation rate and uniform cooling are the main factors that determine the distribution of oxide in copper rod. Uneven cooling causes an essential difference in the internal structure of the Rod, but subsequent hot working often destroys the columnar crystals, making the Cuprous oxide fine and evenly distributed. The typical agglomeration of oxide particles results in a central burst. Except for the influence of oxide particle distribution, the copper rod with smaller oxide particle shows better pulling line characteristics, and the larger CU2O particle is easy to cause stress concentration point and fracture.
The oxygen content of oxygen-free Copper exceeds the standard, the copper rod becomes brittle, the elongation decreases, the tensile port appears dark red, and the crystalline structure is loose. When the oxygen content exceeds 8 PPM, the process performance becomes worse, which shows that the broken rod and broken wire rate increase greatly during casting and drawing. This is due to the oxygen energy forming a Cuprous oxide phase with copper, forming a copper-Cuprous oxide EUTECTIC, which is distributed in a reticular structure on the boundary. Because of its high hardness, the brittle phase will be separated from the copper body during cold deformation, and the mechanical properties of the copper Rod will be reduced. The high oxygen content can also cause the conductivity of the oxygen-free Copper Rod to decrease. Therefore, the casting process and product quality must be strictly controlled.
4. Influence of hydrogen in continuous casting, the content of oxygen is lower, the side effect of oxide is lower, but the influence of hydrogen is more significant. The equilibrium reaction is H2o (G) = [ O ] + 2[ h ] , and the gas and porosity are formed by hydrogen precipitation and aggregation from supersaturated solution during crystallization. The hydrogen released before crystallization can then reduce the Cuprous oxide to form water bubbles. As the up casting is characterized by the crystallization of copper liquid from top to bottom, the shape of the liquid is similar to that of the cone. The gas released before the copper liquid crystallization is blocked in the solidification structure during the floating process, and the gas hole is formed in the casting rod during the crystallization. When the gas content is low, the separated hydrogen exists at the grain boundary and forms porosity, and when the gas content is high, the hydrogen and water vapor form porosity.
Hydrogen comes from various processes in the production process, such as the “Verdigris”of the raw material electrolytic copper, the auxiliary material charcoal * * * , the climatic environment * * * , the undried graphite crystallizer, etc. . Therefore, the surface of molten copper in the melting furnace should be covered with roasted charcoal, and the electrolytic copper should be as far as possible to remove “Copper green”, “Copper beans”and “Ears”, which is very important to improve the quality of oxygen-free copper rods. In the process of continuous casting and rolling, hydrogen is controlled by controlling oxygen content moderately. CU2O + H2 = 2Cu + H2o because the copper melt crystallizes from bottom to top in the casting process, the water vapor produced by oxygen and hydrogen in the copper melt is easy to float out, most of the hydrogen in the copper melt can be effectively removed, so the influence on the copper rod is small.
Second, the surface quality in the production of electromagnetic wire and other products, the surface quality of copper rod also needs to put forward requirements. Need to draw the surface of the copper wire without Burr, less copper powder, no oil pollution. The quality of the surface copper powder was measured by Torsion test and the recovery of the copper rod after torsion was observed to judge its quality. In the process of continuous casting and rolling, the oxide particles are rolled into the surface of copper wire with the rotation of the roll during the rolling process. Because the Cuprous oxide is a brittle compound with a high melting point, when rolled into a deeper Cuprous oxide, when stretched as a strip of polymer in a mold, it causes burrs on the outer surface of the copper rod, causing trouble for subsequent painting. However, the oxygen-free copper rod produced by the up-drawing continuous casting process is completely isolated from oxygen by casting and cooling, and there is no subsequent hot rolling process, and the surface of the copper rod has no oxide rolled into the surface.
The oxygen-free Copper Rod is also divided into imported equipment and domestic equipment, but at present, the imported products have no obvious advantages. The difference after the copper rod products come out is not very big. As long as the copper plate is well selected, the production control is relatively stable, domestic equipment can also produce 0.05 tensile copper Rod. Imported equipment is generally Otokumpu Finland’s equipment, the best domestic equipment should be the Shanghai Navy factory, the longest production time, military enterprises, reliable quality. There are two kinds of import equipment of low oxygen copper Rod, one is American south line equipment, English is SOUTHWIRE, the domestic factory is Nanjing Huaxin, Jiangxi Copper Industry, the other is German CONTIROD equipment, the domestic factory is Changzhou Jin Yuan, Tianjin seamless.
Oxygen-free and low oxygen rod from oxygen content is easy to distinguish, oxygen-free copper is oxygen content in 10-20 PPM below, but some manufacturers can only do 50 PPM below. Low Oxygen Copper Rod in 200-400 PPM, good rod general oxygen content control in 250 PPM or so, non-oxygen rod general is to take the lead method, low oxygen rod is continuous casting and continuous rolling, two products relatively low oxygen rod to enamelled linear, can adapt some, such as flexibility, springback angle, winding performance. But the low-oxygen rod is relatively harsh on the drawing conditions, the same draw 0.2 of the fine wire, if the drawing line condition is not good, the ordinary oxygen-free rod can be drawn and the Good low-oxygen rod will break the line, but if the good drawing line condition is put, the same Rod, a low-oxygen rod might pull a double-zero-five, whereas an ordinary oxygen-free rod can only stretch to 0.1, and of course the thinnest ones like double-zero-two have to rely on imported, oxygen-free copper rods. At present, some enterprises try to use the method of peeling to deal with Hypoxia rod to extend 0.03 line. But I don’t know much about that.
Low Oxygen Copper Rod sound generally prefer to use oxygen-free Rod, and oxygen-free rod is single crystal copper, low oxygen rod is polycrystalline copper related. The low oxygen copper Rod and the oxygen-free Copper Rod have their own characteristics because of the different manufacturing methods. The oxygen content of Cathode Copper for copper rod production is generally 10 ~ 50 PPM, and the solubility of oxygen in copper at room temperature is about 2 ppm. The oxygen content of the low oxygen copper rod is generally 200(175) to 400(450) PPM, so the oxygen is absorbed in the liquid state of copper, whereas the oxygen-free Copper Rod is reduced and removed after the oxygen has been kept in the liquid state of copper for a long time, the oxygen content of the Rod is usually under 10.50 PPM, with a minimum of 1-2 PPM. The oxygen in low oxygen copper exists near the grain boundary in the form of copper oxide, this may be common for low oxygen copper bars but is rare for oxygen free copper bars. The appearance of copper oxide in the grain boundary as inclusion has a negative effect on the toughness of the material. Oxygen in oxygen-free copper is very low, so the copper structure is uniform single-phase structure is conducive to toughness. POROSITY is uncommon in oxygen-free copper rods and a common defect in low oxygen copper rods.
2. The difference between the hot-rolled structure and the cast structure the structure of the low oxygen copper rod is a hot-worked structure because it has been hot-rolled. The original cast structure has been broken, and the form of recrystallization has appeared when the rod is 8 mm long, the oxygen-free copper rod is a cast structure with coarse grain, which is the inherent reason why oxygen-free copper has higher recrystallization temperature and needs higher annealing temperature. This is because recrystallization takes place near the grain boundary. The microstructure of the oxygen-free copper rod is coarse, and the grain size can even reach several millimeters, so the grain boundary is less. Even though drawing deformation, the grain boundary is less than the oxygen-free Copper Rod, therefore, high annealing power is required. The requirement for successful annealing of oxygen-free copper is that the annealing power of the first annealing is 10-15% higher than that of low-oxygen copper when the wire is drawn by a rod but not yet cast. After further drawing, there should be enough allowance for annealing power at later stage and different annealing processes should be carried out to ensure the softness of in-process and finished wire.
3. Inclusion, fluctuation of oxygen content, difference between surface oxide and possible hot-rolled defects. The tensile properties of oxygen-free Copper Rod are superior to those of low oxygen copper rod in all wire diameters, the oxygen content is stable, and the thickness of the oxide on the rod surface is less than 15A. In the process of continuous casting and rolling, if the process is unstable, the monitoring of oxygen is not strict, and the oxygen content is unstable, the properties of the rod will be affected directly. If the oxide on the surface of the Rod can be made up in the continuous cleaning of the post-process, but the more troublesome thing is that there are quite a lot of oxide in the “Subcutaneous”, which has a more direct influence on the breakage of the pull wire, so when drawing the micro wire, the ultra-micro wire, in order to reduce wire breakage, sometimes we have to take the method of copper rod-peeling, or even the reasons for the second peeling, to remove the oxide under the skin.
4. The toughness of low oxygen copper Rod and Oxygen Free Copper Rod is different, both of them can be drawn to 0.015 mm, but the distance between the wires of low temperature oxygen free copper in low temperature superconductor is only 0.001 mm. There is a difference in the economy from the raw material of the rod to the wire. High quality raw materials are required for the manufacture of oxygen-free copper rods. In general, when drawing copper wire with diameter & GT; 1mm, the advantage of low oxygen copper rod is obvious, but the advantage of non oxygen copper rod is drawing copper wire with diameter & Lt; 0.5mm. The wire making technology of low oxygen copper rod is different from that of Oxygen Free Copper Rod. The wire-making process of low oxygen copper rod can not be copied to the wire-making process of oxygen-free Copper Rod, at least the annealing process is different. Because the flexibility of the wire is greatly affected by the material composition and rod making, wire making and annealing process, it can not be said simply that low oxygen copper or oxygen-free copper who is soft and hard. ATTACHED: brief introduction of low oxygen copper Rod and Oxygen Free Copper Rod
1. Low Oxygen Copper Rod what is a low oxygen copper rod? What is the production process of low Oxygen Copper Rod? What is the brief introduction of low Oxygen Copper Rod? First look at the definition of low oxygen copper rod: Copper Rod with oxygen content between 200(175) and 400(450) PPM was produced by continuous casting and rolling of copper as raw material. Low Oxygen Copper Rod introduction-low Oxygen Copper Rod process flow: Low Oxygen Copper Rod is produced by continuous casting and rolling process, the technological process is as follows: Electrolytic Copper → Shaft Furnace → holding furnace → casting machine → continuous rolling mill → cleaning → receiving rod machine → finished product (8mm) electrolytic copper is continuously fed, copper water is discharged after continuous melting in shaft furnace, and large section trapezoidal ingots are cast by casting machine, enter the rolling mill for Hot Rolling, rolling into 8 copper rod billet. Process Defects (1) shaft furnace: A:. Due to the small size of the shaft furnace, the electrolytic copper is melted with the addition of the side melt, and the molten copper water has no condition for full reduction. “B.”. . The oxygen content is very high during the whole melting process and the copper-producing water process . . C. Molten copper fuel is generally gas, gas combustion process, will directly affect the chemical composition of copper liquid treatment, the greater impact of sulfur and hydrogen. (2) casting machine: Casting machine crystallization wheel will become solid copper liquid process, can not carry out oxygen isolation, so the casting process for a second large amount of oxygen.
Temperature control: A. The temperature of liquid copper is not easy to control because of the large rolling amount and the restriction of many factors. B. The ingot temperature of the rolling mill should be controlled at 850 °C. The larger the up-down deviation is, the greater the influence on the quality of the copper rod is. C. It is difficult to control the temperature of the copper rod of the rolling mill because of the restriction of the former working procedure. D. There are many links in the whole process, and some links slightly appear some problems, will affect the temperature control. (4) others: A. Because of the above-mentioned defects, the quality of copper rod will be unstable, so the standard: continuous casting and rolling low oxygen copper rod before leaving the factory, must do a torsion test. But some factories do not do, or not according to the provisions of batch to do (each batch should not exceed 60 tons) , or to reverse the unqualified batch still factory. B. High oxygen content, will affect the drawing process, copper wire more and more hard, in the middle to increase annealing. High oxygen content also affects electrical conductivity. C. In order to solve the process defects, as far as possible to improve the unit performance, so the unit price pleiades expensive. For example, the American Southern Line Company produces 24,000 to 40,000 tons of units per year, with a price of 6.9 million US dollars. The German Krupp Company is even more expensive. The user’s own amenities will cost between one hundred thousand and one million. Process advantages: (1) high output, general small unit output per hour up to 10 ~ 14 tons. (2) the copper rod unloading line adopts plum-blossom type, which is convenient for the laying-out of the pulling line machine. (3) heavy take-up, usually up to 4 tons per plate.
1. dip-coating method: it can produce large length bright oxygen-free Copper Rod, conductivity is 101 ~ 102% IACS, oxygen content is below 20 PPM, weight of copper rod ring is 3.5 ~ 10 tons. By using the heat absorbing ability of the Cold Copper Rod, a thin cold pure copper core Rod (or seed Rod) is used to melt the copper water with the surface copper of the moving seed rod vertically through a copper pool which can keep a certain liquid level high and low, then it is cooled, hot-rolled, cooled and wound into a coil. The whole process is closed and protected by inert gas. 2. Cold Rolling method: Can Produce Large length bright oxygen-free Copper Rod, conductivity 101 ~ 101.6% IACS, oxygen content below 10 PPM, copper Rod Ring Weight 2 tons. It uses a tubular copper sleeve (that is, a graphite crystallizer) , the lower end of which extends into and immerses under the molten copper level, the upper end is communicated with a vacuum pump, and the air in the crystallizer is initially pumped out, under the action of vacuum, a negative pressure is generated in the tube, the liquid copper is slowly drawn upward and soon solidifies into a bright ingot near the elevator. And then cold-rolled or cold-drawn into rods. Copper Rod produced by up-drawing method has a bright surface with oxygen content below 10 PPM. 3. Continuous casting and rolling method: Can Produce Large length bright low oxygen copper Rod, conductivity 101 ~ 102% IACS, oxygen content 200 ~ 300 PPM, copper rod ring weight up to 5 tons. 4. Loop rolling method: Producing Black Copper Rod with short length oxide scale, the conductivity is 99.5 ~ 100.5% IACS, oxygen content is 200 ~ 500 PPM, the weight of the copper rod ring is only 86 ~ 136 kg. Restricted by weight of ship-shaped copper ingots
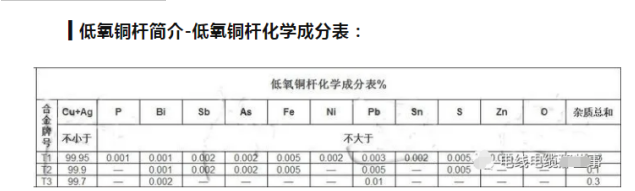
Low Oxygen Copper Rod brief introduction-low Oxygen Copper Rod grades and characteristics: Low Oxygen Copper Rod grades have three types, t 1, t 2, T 3, low oxygen copper rod are hot rolled, so it is a soft Rod, code R. (1) T 1: Producing Low Oxygen Copper Rod with high purity electrolytic copper (containing more than 99.9975% copper) . (2) T2: Using 1 # electrolytic copper as raw material (containing more than 99.95% copper) to produce low oxygen copper Rod. (3) T3: Using 2 # electrolytic copper as raw material (containing more than 99.90% copper) to produce low oxygen copper Rod. Because the market of high pure electrolytic copper and 2 # electrolytic copper is very few, generally using 1 # electrolytic copper as raw material, so the general low oxygen copper rod brand is: T2r.
2. The oxygen content and appearance of the oxygen-free Copper Rod are different because of the different technology of producing the copper Rod. The copper rod produced by continuous casting and rolling is hot rolled under protective conditions with oxygen content in the range of 200-500 PPM, but sometimes up to 700 PPM or more, the copper produced by this method has a bright appearance and is commonly known as a Bright Rod. The oxygen-free copper rod is pure copper without oxygen and without any deoxidizer residue. But it actually contains very little oxygen and some impurities. According to the standard, the oxygen content is not more than 0.02% , the total impurity content is not more than 0.05% , the purity of copper is more than 99.95% . Generally produced with electrolytic copper, the resistivity is lower than the low oxygen copper Rod, so in the production of more demanding resistance products, oxygen-free Copper Rod is more economical; The advantage of oxygen-free copper rod is drawing copper wire with diameter & Lt; 0.5 mm. 6MM oxygen-free copper rod is used to produce flat copper wire. 3mm oxygen-free Copper Rod for wire drawing, production of copper wire, enamelled wire. Mainly used in wire, cable and motor. According to the oxygen content and impurity content, the oxygen-free copper rods are divided into TU1 and TU2 copper rods. The purity of Tu1 oxygen-free copper rod is 99.99% , oxygen content is not more than 0.001% , the purity of TU2 oxygen-free copper rod is 99.95% , oxygen content is not more than 0.002% .
Source: cables, wires, things like that
Disclaimer: Some pictures and texts on this site are collected from the Internet and are only for learning and communication. The copyright belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of our site. This site will not bear any legal responsibility. If your rights are violated, please contact us to delete it in time.


